GHG Protocol Software: Innovations in Carbon Accounting
Introduction
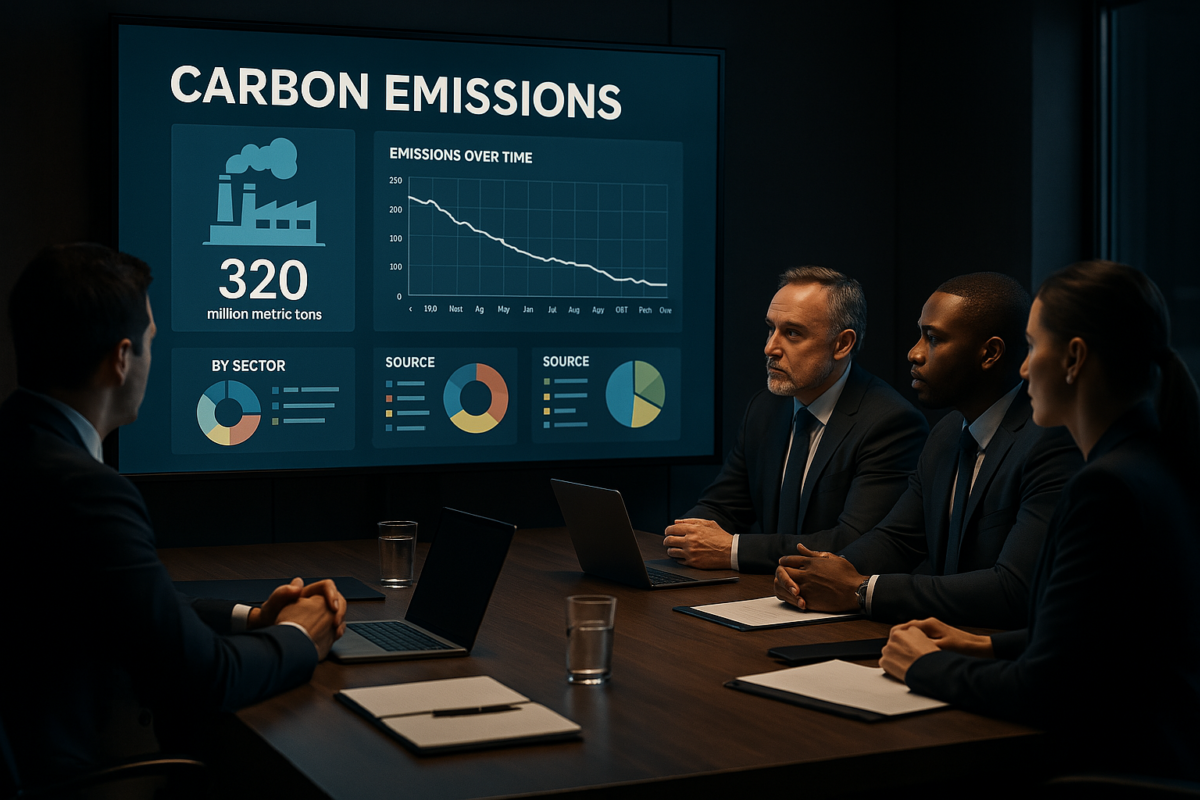
Ensuring accurate and transparent greenhouse gas emissions reporting is essential for corporate climate accountability. GHG protocol software plays a pivotal role in helping organizations meet compliance standards while enhancing sustainability efforts. This blog explores the innovative tech behind GHG compliance tools, carbon accounting tech, and how these advancements empower companies with precise, scientific emissions reporting and robust ESG reporting software.
Understanding GHG Protocol Compliance
The GHG Protocol Software provides a globally accepted framework for measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions. Compliance requires detailed data collection, standardized reporting, and adherence to regulatory norms.
Modern GHG compliance tools automate this complex process by integrating data from multiple sources and applying scientific methodologies for:
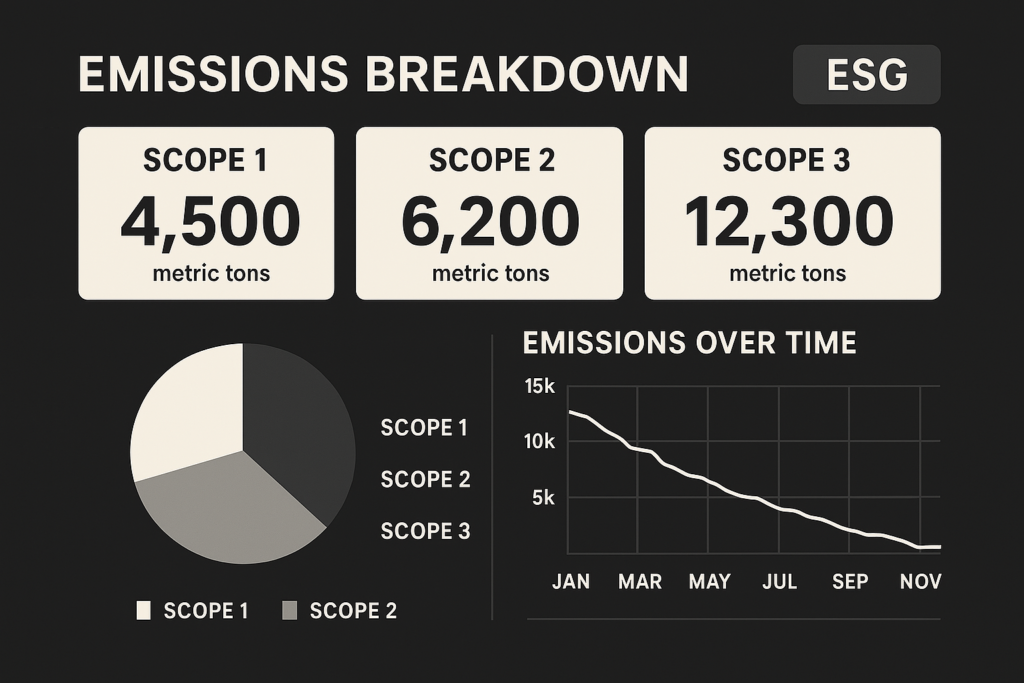
- Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions tracking
- Emissions factor calculations
- Validation and verification of reported data
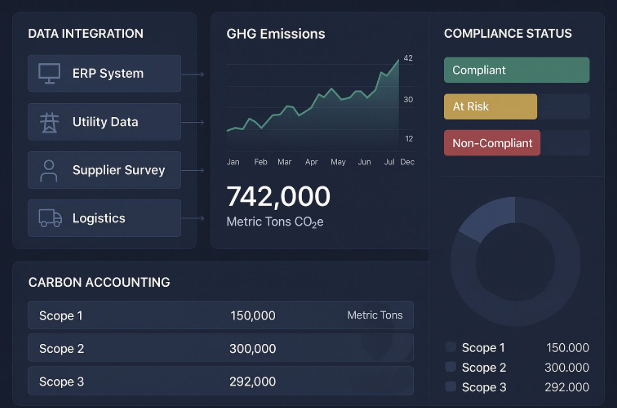
Core Technologies Powering GHG Protocol Software
1. Advanced Data Integration & Automation
- Seamless import of emissions data from ERP systems, IoT sensors, and external databases
- Automated data validation reduces manual errors and improves accuracy
2. Scientific Emissions Tools & Analytics
- Use of precise emissions factors based on scientific research
- AI and machine learning analyze trends and detect anomalies
3. Blockchain for Transparency
- Immutable carbon ledger technology ensures data integrity
- Enables transparent audits and stakeholder trust
4. Cloud-Based Platforms
- Scalable software accessible across global operations
- Real-time reporting and updates for compliance readiness
How Carbon Tracking Innovations Improve ESG Reporting
Innovations in carbon accounting tech and ESG reporting software are enabling organizations to:
- Track emissions more precisely across their value chains
- Provide granular emissions data for scientific emissions tools to analyze
- Automate ESG disclosures aligned with regulatory frameworks
- Enhance forecasting and scenario modeling for climate risk
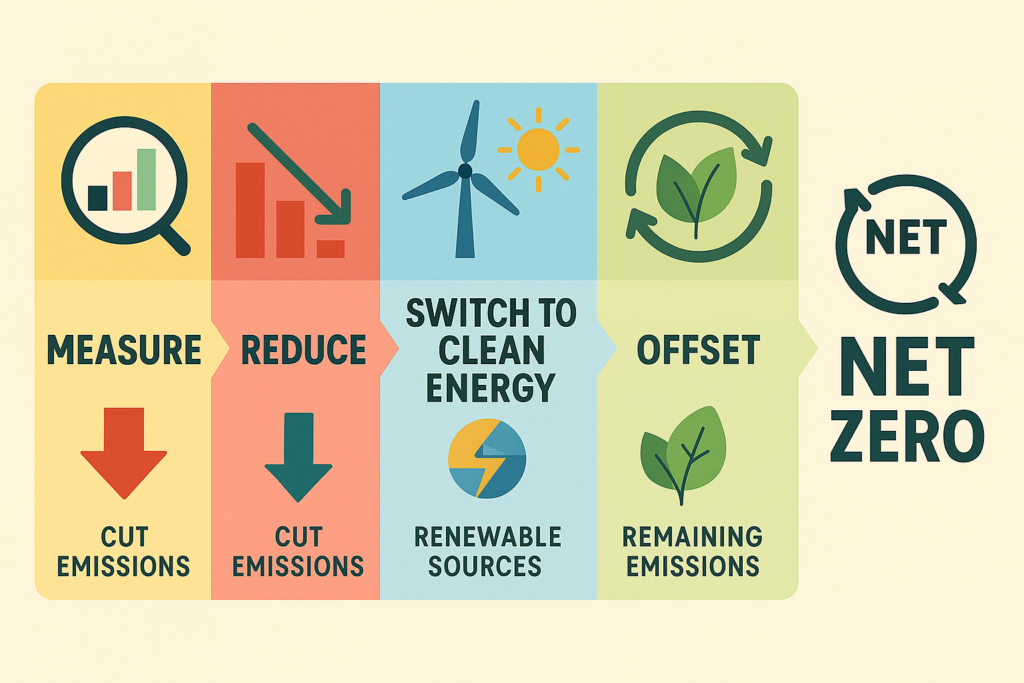
Benefits of Using GHG Protocol Compliance Software
| Benefit | Description |
| Improved Accuracy | Automated data collection and scientific calculations |
| Regulatory Compliance | Aligns with global standards like the GHG Protocol |
| Enhanced Transparency | Blockchain and audit-ready data improve trust |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces manual reporting workload and errors |
| Strategic Insights | Analytics and AI-driven predictions support decision-making |
Challenges & Solutions in GHG Emissions Reporting
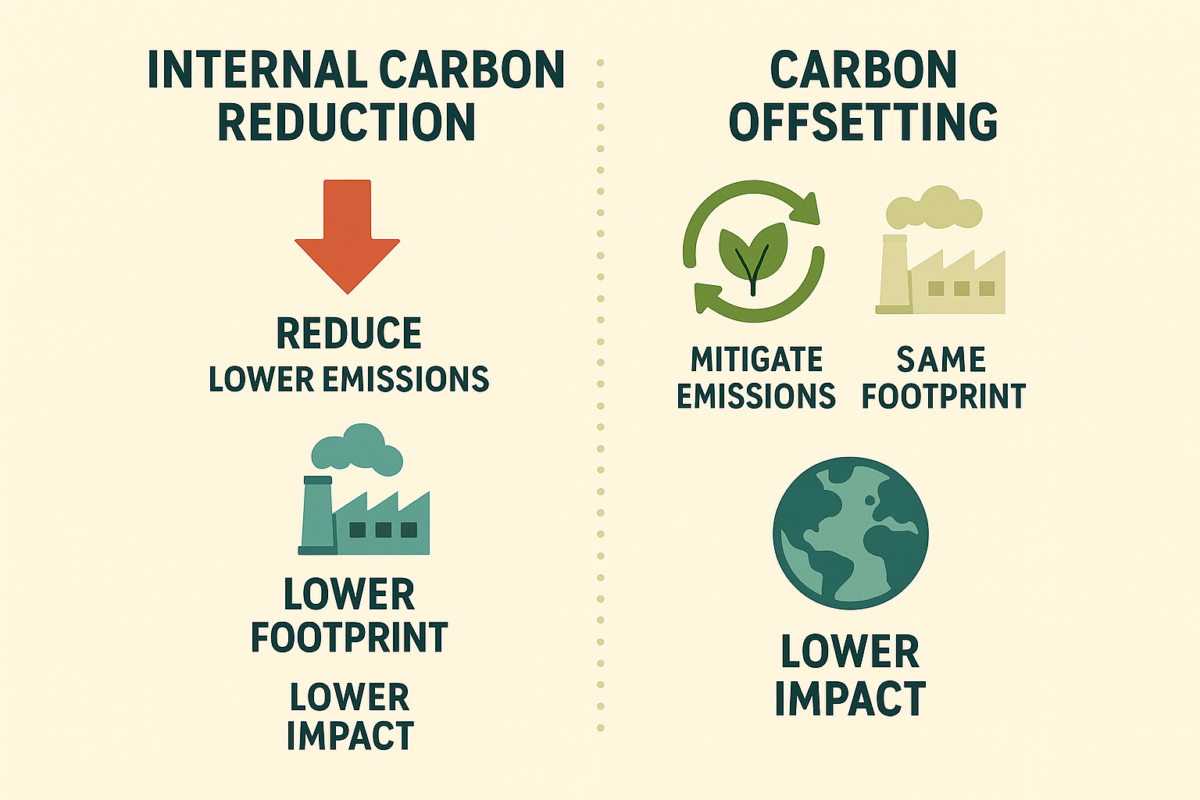
- Data Fragmentation: Addressed by integrated platforms consolidating all emission sources
- Verification Complexity: Streamlined through AI-based data validation and blockchain audit trails
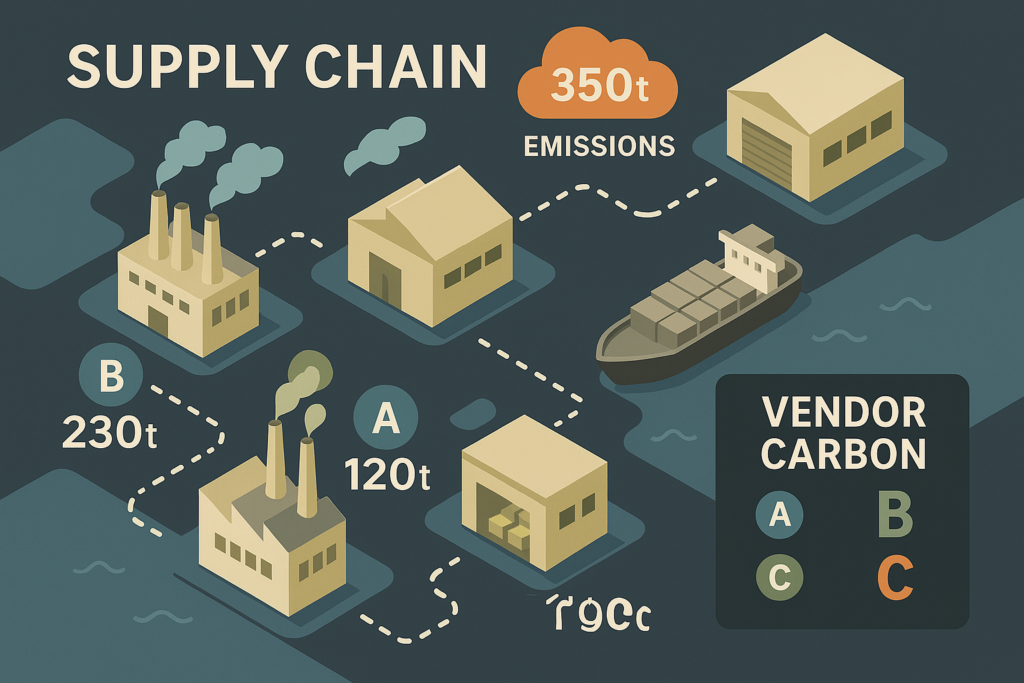
- Scope 3 Reporting: Enhanced with supplier engagement and carbon lifecycle analytics
Real-World Impact: Case Studies
Global Manufacturing Leader
Implemented GHG protocol software to automate emissions reporting across 50+ sites worldwide, reducing reporting errors by 40% and accelerating compliance timelines.
Financial Services Firm
Used ESG reporting software with AI analytics to meet investor demands for transparent, real-time emissions disclosures, improving ESG scores and stakeholder confidence.
ALSO READ: Carbon Capture and the Physics: What ESG Tools Must Track
Future Trends in GHG Compliance Technology
- Increased use of predictive analytics for emissions forecasting
- Integration of IoT sensors for real-time carbon tracking
- Expansion of blockchain applications in sustainability reporting
- Greater emphasis on user-friendly dashboards and mobile accessibility
FAQs
Q1: What is the primary role of GHG protocol software?
A1: It ensures standardized, accurate measurement and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions to comply with global standards.
Q2: How do blockchain technologies enhance GHG compliance tools?
A2: By providing immutable records of emissions data, ensuring transparency and auditability.
Q3: Can GHG compliance software handle Scope 3 emissions?
A3: Yes, modern platforms include features to track and analyze Scope 3 emissions through supply chain data integration.
Call to Action
Ready to elevate your carbon accounting with cutting-edge GHG protocol software? Contact our experts today to explore tailored ESG tech solutions that simplify emissions compliance and boost your sustainability strategy.