Real-Time Carbon Data and it’s Science: Why It Matters
Introduction
In an era where climate action depends on precision and transparency, real-time carbon data is transforming how organizations monitor their carbon footprint. Unlike traditional periodic reporting, real-time emissions tracking software offers up-to-the-minute insights, enabling faster decision-making and more effective climate strategies.
This article explains the science behind real-time carbon data, its impact on scientific ESG reporting, and how advanced carbon accounting technology and climate data software are revolutionizing emissions management for businesses worldwide.
What is Real-Time Carbon Data?
Real-time carbon data refers to the continuous, instantaneous measurement and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through sensors, IoT devices, and connected software systems.
Traditional carbon accounting relies on periodic data collection—monthly, quarterly, or annually. Real-time data, however:
- Captures emissions as they occur
- Enables immediate identification of anomalies
- Provides granular visibility into carbon sources and sinks
The Science Behind Real-Time Emissions Tracking
Accurate emissions tracking software depends on several scientific and technological advances:
- Sensor Technologies: Infrared gas analyzers, laser-based spectrometers, and chemical sensors detect CO₂, CH₄, and other GHGs continuously.
- Data Integration: Combining IoT devices with cloud computing ensures seamless real-time data transmission and storage.
- Advanced Algorithms: AI and machine learning analyze streaming data for noise reduction, calibration, and anomaly detection.
- Carbon Flux Modeling: Models simulate carbon lifecycle and emission sources to contextualize raw sensor data scientifically.
Why Real-Time ESG Data Matters
Enhanced Decision-Making
Access to real-time ESG data empowers sustainability teams to:
- Quickly address unexpected emission spikes
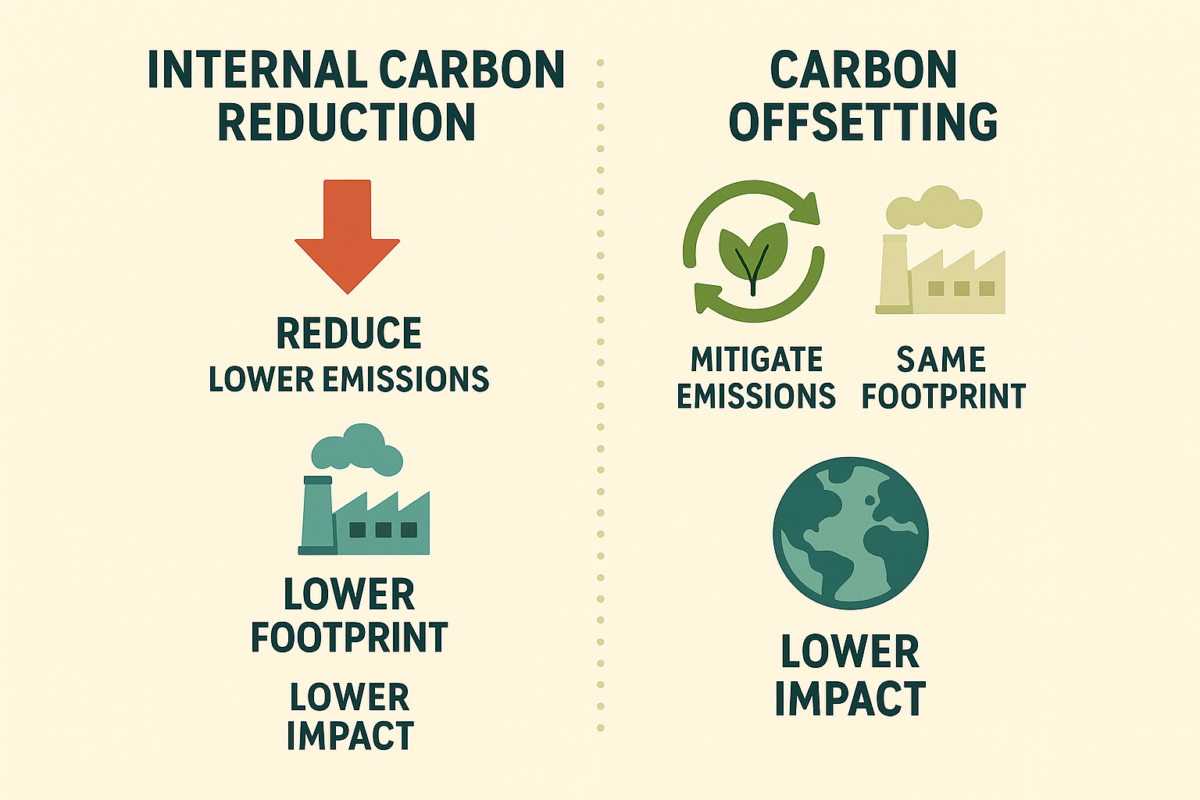
- Optimize operational processes for carbon reduction
- Validate effectiveness of carbon offset projects
Improved Regulatory Compliance
Regulators increasingly require transparent, timely emissions disclosure. Real-time data supports compliance with:
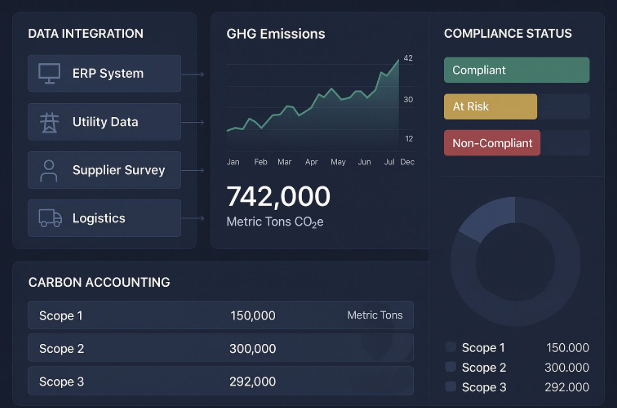
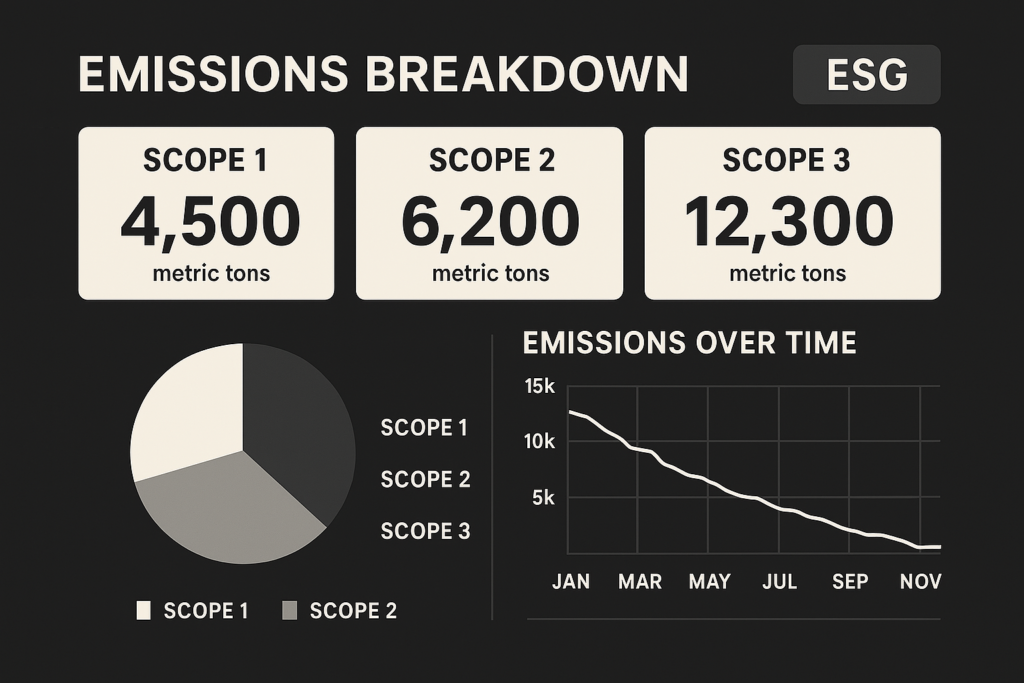
- GHG Protocol and Scope 1, 2, 3 emissions reporting
- Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
- European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)
Increased Stakeholder Trust
Investors and customers demand accurate, up-to-date climate data. Real-time emissions data enhances:
- ESG ratings accuracy
- Public reporting credibility
- Corporate climate accountability
Integrating Real-Time Carbon Data into Carbon Accounting Technology
To leverage real-time data fully, organizations integrate emissions tracking with comprehensive carbon accounting technology, including:
- Data normalization to align sensor inputs with emission factors
- Lifecycle assessment (LCA) tools for comprehensive carbon footprint analysis
- Emissions management platforms that unify data across facilities and geographies
- Predictive analytics to forecast emissions trends and compliance risks
This integration enables scientific ESG reporting that is not only accurate but predictive and adaptive.
ALSO READ: Carbon Capture and the Physics: What ESG Tools Must Track
Key Benefits of Real-Time Carbon Footprint Monitoring
- Granular Visibility: Break down emissions by process, equipment, or location.
- Rapid Response: Mitigate risks and operational inefficiencies immediately.
- Continuous Improvement: Use live data to drive ongoing sustainability initiatives.
- Transparency: Facilitate robust stakeholder reporting and audits.
Challenges in Real-Time Emissions Management
| Challenge | Solution |
| High data volume and complexity | Employ AI-powered data filtering and visualization |
| Sensor calibration and accuracy | Routine maintenance and cross-validation with manual sampling |
| Integration with legacy systems | Use APIs and middleware for smooth data exchange |
| Data security and privacy | Implement encryption and secure cloud protocols |
Real-World Applications of Real-Time Carbon Data
Manufacturing Industry
Factories use real-time carbon footprint monitoring to reduce energy waste and track emissions in production lines, enabling compliance with local environmental laws.
Energy Sector
Power plants leverage emissions tracking software integrated with carbon accounting tech to monitor combustion efficiency and optimize fuel use.
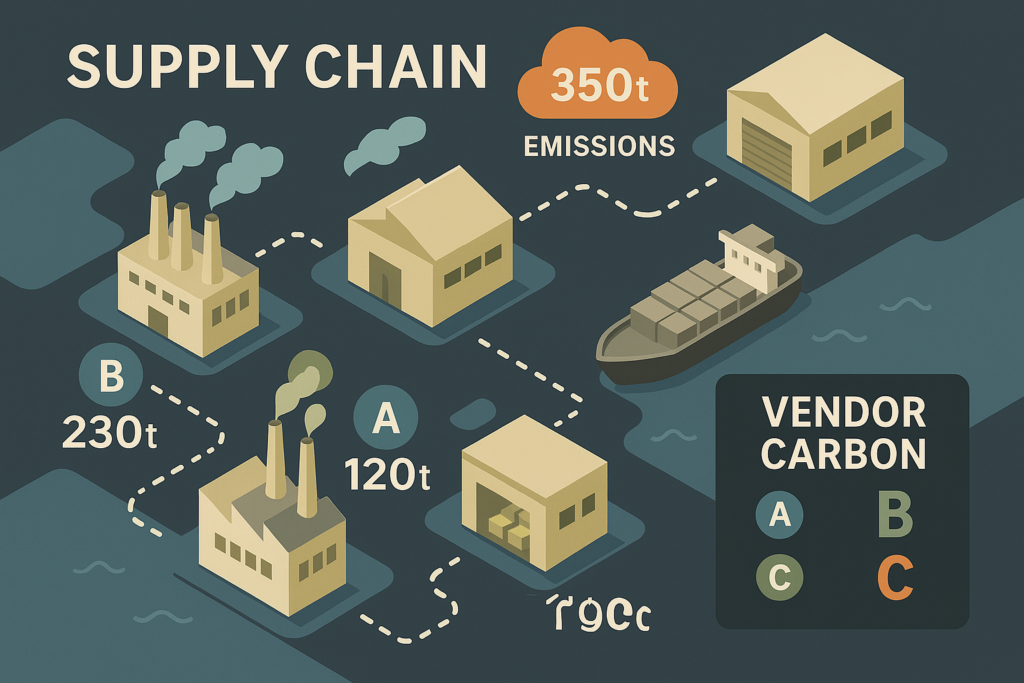
Supply Chain Monitoring
Companies implement real-time data to track Scope 3 emissions across suppliers, providing transparency and reducing hidden carbon risks.
Future Trends in Real-Time Carbon Data and ESG Analytics Software
- Edge Computing: Processing emissions data closer to the source for faster insights.
- Blockchain Integration: Securing real-time data with immutable ledgers.
- AI-Powered Forecasting: Using historical and live data to predict future emissions scenarios.
- IoT Expansion: Wider deployment of smart sensors across sectors.
FAQs
How does real-time carbon data improve emissions accuracy?
It minimizes manual errors and reporting delays by capturing continuous, sensor-based measurements directly from emission sources.
Can real-time emissions tracking software handle Scope 3 emissions?
Yes, by integrating supplier data streams and applying carbon lifecycle analytics, real-time tools enhance Scope 3 transparency.
Is real-time ESG data expensive to implement?
Costs vary, but scalable IoT and cloud solutions make real-time emissions tracking increasingly accessible for mid-size and large organizations.
Call to Action
Unlock the power of real-time carbon data to advance your sustainability goals with cutting-edge emissions tracking software and ESG analytics tools. Contact us today to schedule a demo and transform your carbon accounting processes.