The Importance of Carbon Accounting Certification in 2025

Introduction
In an age where climate change and sustainability are taking center stage, businesses must adopt strategies that not only foster growth but also promote environmental responsibility. Carbon accounting certification has emerged as one of the most crucial elements for businesses aiming to meet these sustainability goals. It is no longer enough for companies to simply reduce their carbon footprint; they need to track, measure, and report their emissions with transparency and accuracy. Achieving carbon accounting certification not only shows a business’s commitment to sustainability but also ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
For organizations seeking to make a positive impact on the environment, earning carbon accounting certification is a major step toward proving their dedication to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The certification process involves a comprehensive audit of a company’s carbon emissions, focusing on how effectively they are being monitored and reduced over time. In this article, we will explore why carbon accounting certification is essential, the process involved, and how it benefits businesses in the long run.
What is Carbon Accounting Certification?
Carbon accounting certification refers to the formal validation of a company’s carbon footprint measurement and reduction efforts. It is awarded by third-party organizations that follow internationally recognized standards. The certification process ensures that a business’s carbon footprint is calculated accurately, its emissions data is reported in a transparent manner, and appropriate steps are being taken to reduce emissions.
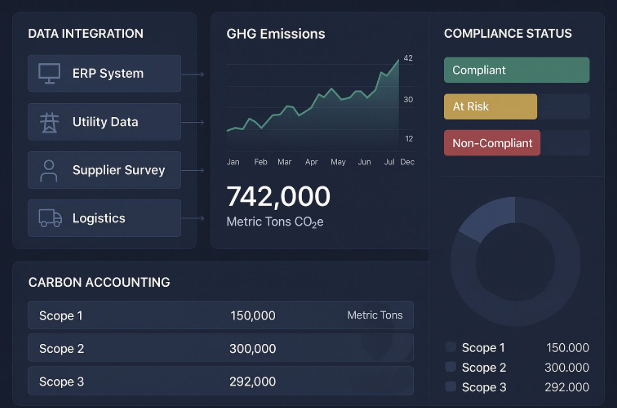
This certification can apply to various scopes of emissions, from direct emissions produced by the company (Scope 1), to indirect emissions from purchased electricity (Scope 2), and further indirect emissions from the company’s value chain, including suppliers and customers (Scope 3). By obtaining this certification, a company demonstrates its commitment to environmental sustainability and ensures that it is meeting regulatory standards for carbon emissions reporting.
The significance of carbon accounting certification lies in its ability to help businesses manage their environmental impact and move towards carbon neutrality. For a business to be considered truly sustainable, it needs to take proactive measures to measure, reduce, and offset carbon emissions across its entire supply chain.
Why Certification Matters for Businesses
1. Boosting Corporate Reputation
In today’s competitive marketplace, companies are increasingly being judged by their commitment to sustainability. Customers, investors, and stakeholders are now looking beyond the products or services a company offers—they are also considering how the company operates in relation to environmental impact. Companies that are transparent about their carbon emissions and demonstrate an ongoing effort to reduce them often enjoy a positive reputation among consumers.
Having carbon accounting certification allows a company to showcase its environmental responsibility. It is a strong signal to both customers and investors that the company is committed to reducing its carbon footprint and contributing positively to the environment. Businesses that can provide proof of their carbon emissions and mitigation strategies often experience increased customer loyalty, stronger brand equity, and heightened appeal to eco-conscious investors.
2. Meeting Regulatory Requirements
As governments around the world continue to implement stricter environmental regulations, businesses must remain vigilant in ensuring they meet the required standards. Carbon accounting certification helps businesses navigate this regulatory landscape by providing a clear framework for calculating, reporting, and reducing carbon emissions.
In many countries, there are laws and regulations in place that require businesses to report their carbon emissions. Certification provides assurance that a company is following the necessary processes to comply with local and international environmental standards. It also ensures that businesses are prepared for future regulatory changes that may require them to track and reduce their carbon emissions more extensively.
3. Attracting Eco-Conscious Investors
Investors today are increasingly looking for businesses that prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility. Many investment firms, particularly those focused on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, favor companies with verified sustainability efforts. Carbon accounting certification acts as proof that a company is committed to its environmental goals and can be trusted to follow through on its promises.
By obtaining certification, businesses signal to potential investors that they are a reliable, responsible, and forward-thinking company. Furthermore, being carbon certified opens doors to funding opportunities from eco-conscious investors who prefer to support businesses that have a proven track record of environmental responsibility.
4. Improving Operational Efficiency
One of the often-overlooked benefits of carbon accounting certification is the operational efficiency it drives. Through the certification process, businesses identify inefficiencies in their operations that contribute to high levels of emissions. Once identified, steps can be taken to optimize processes, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste—all of which can lead to cost savings.
For example, businesses may find that they are overusing energy in certain areas of operations or that certain emissions reduction technologies can be implemented to cut back on energy costs. These optimizations help businesses become more cost-effective while simultaneously contributing to global sustainability efforts.
The Certification Process
Achieving carbon accounting certification involves several critical steps, each designed to ensure that businesses are accurately measuring their carbon emissions and taking appropriate steps to reduce them. The following is an overview of the process involved in earning certification:
1. Measuring the Company’s Carbon Footprint
The first step toward obtaining certification is to accurately measure the company’s carbon footprint. This involves calculating the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions produced by the business, including direct emissions (Scope 1), indirect emissions from purchased electricity (Scope 2), and emissions from other activities like the supply chain and transportation (Scope 3).
Using specialized tools and software, companies collect data on their energy usage, waste production, transportation emissions, and any other activities that contribute to their overall carbon footprint. This data is then compiled into a comprehensive report that serves as the foundation for the certification process.
2. Reporting Emissions Data
Once the carbon footprint has been measured, businesses must report their emissions data to a third-party certifying body. The report typically includes detailed information about the sources of emissions, the strategies used to reduce emissions, and any goals set for future reductions.
Third-party organizations that provide carbon accounting certification will evaluate the emissions data to ensure accuracy and transparency. The company must demonstrate that the data is collected and reported in accordance with established carbon accounting standards.
3. Implementing Carbon Reduction Strategies
After measuring and reporting emissions, businesses need to show that they have taken concrete steps to reduce their environmental impact. This could involve:
- Energy efficiency initiatives such as upgrading to energy-efficient lighting or equipment.
- Switching to renewable energy sources, like solar or wind.
- Sustainable supply chain practices that reduce emissions in procurement and logistics.
A business’s carbon reduction strategies are evaluated as part of the certification process to ensure that they are both effective and aligned with industry standards.
4. Undergoing Third-Party Audits
A key component of the certification process is a third-party audit. An independent auditor will review the company’s emissions data, carbon reduction efforts, and overall sustainability practices to ensure compliance with the certifying body’s standards.
This audit serves as an external validation of the company’s claims and helps establish credibility for businesses looking to gain the trust of customers and investors.
Benefits of Carbon Accounting Certification
The long-term benefits of carbon accounting certification for businesses are numerous. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Compliance with Regulations:
With global governments tightening carbon emissions regulations, certification helps businesses stay ahead of regulatory requirements and avoid costly fines or penalties.
2. Enhanced Brand Trust:
Having carbon accounting certification helps build trust with customers, employees, and investors, showing that the business is committed to environmental sustainability.
3. Cost Savings:
By identifying areas where emissions can be reduced, companies can implement energy-saving strategies that result in cost savings over time.
4. Sustainability Leadership:
Certification positions businesses as leaders in corporate sustainability, helping them stand out in an increasingly competitive and environmentally-conscious market.
Conclusion
Carbon accounting certification is an essential process for businesses looking to make a tangible impact on the environment while also enhancing their operational efficiency and corporate reputation. By following the steps outlined in the certification process, companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and carbon neutrality. As environmental regulations become stricter, obtaining carbon accounting certification will become increasingly vital for businesses looking to stay competitive and compliant.
Get Certified Today
Ready to earn your carbon accounting certification? Subscribe to our newsletter for tips on achieving certification, or download our guide to start your journey toward sustainability today!