Carbon Offset Myths: Net Zero Requires More
Introduction
Many businesses rely on carbon offset programs to meet their sustainability targets. While offsets can support environmental projects, they are not a silver bullet. Reaching true net zero emissions requires deeper action. Companies must reduce emissions at the source, integrate science-based strategies, and use offsets as a last resort. This article breaks down the limitations of offsetting and outlines a more reliable path to meaningful climate results.
What Are Carbon Offset Programs?
Carbon offsets are credits businesses purchase to compensate for their emissions. One credit typically equals one tonne of CO2 avoided or removed. These programs support various projects such as reforestation, renewable energy, and methane capture. Although helpful, offsets do not eliminate the actual emissions a company produces. They are external solutions, often far removed from the company’s operations.
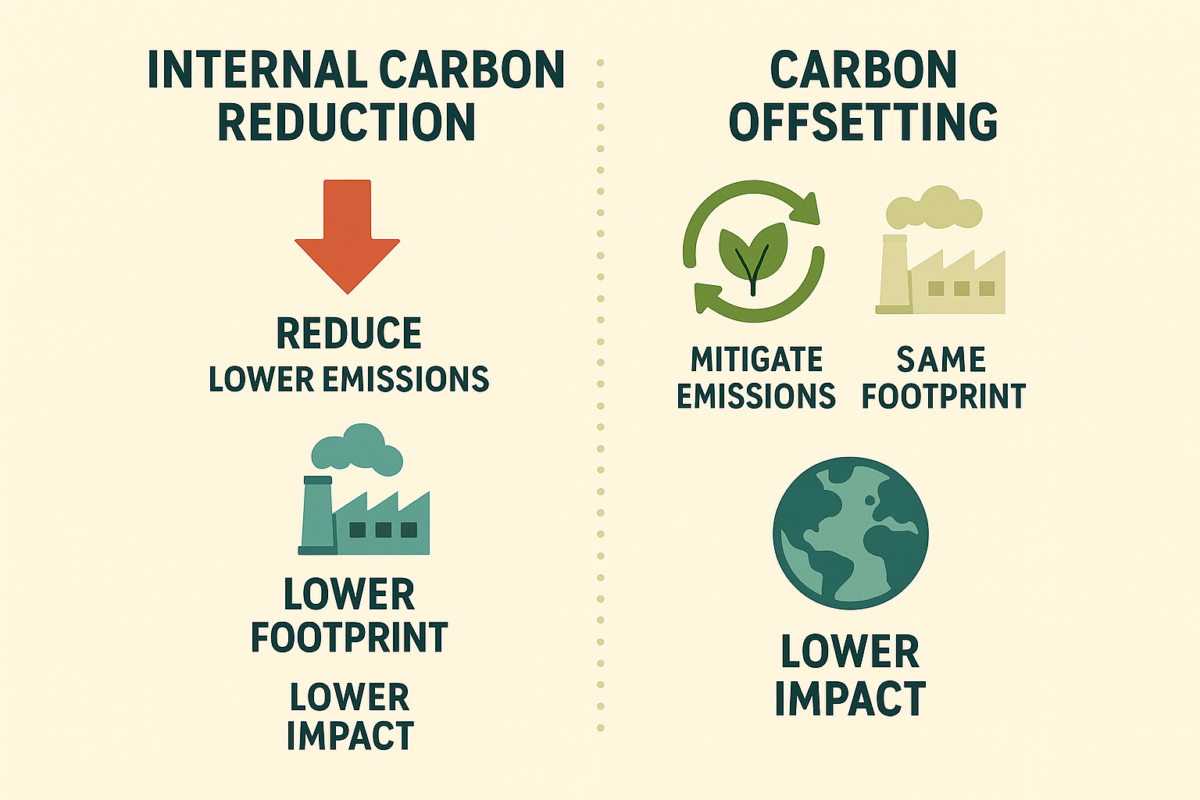
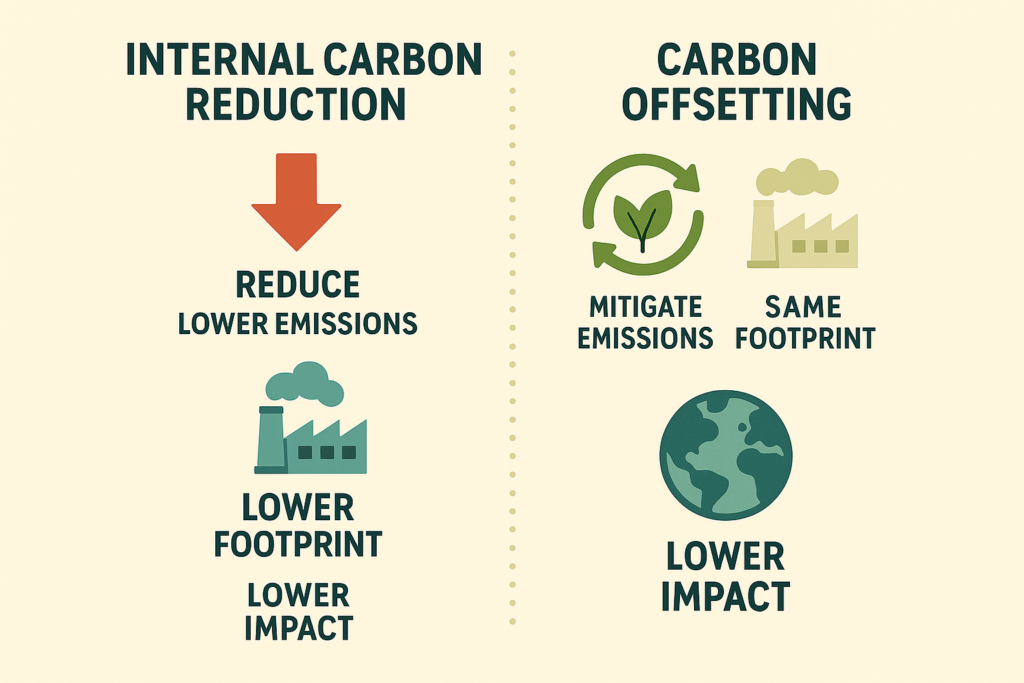
The Illusion of Carbon Neutrality
Using offsets alone can create a false impression of carbon neutrality. Companies may continue emitting while claiming environmental responsibility. This leads to accusations of greenwashing. More importantly, it delays the urgent need for emission reduction. Relying solely on carbon credits is like covering a leaking pipe with duct tape, a temporary fix, not a solution.
Why Carbon Reductions Must Come First
To achieve net zero emissions, internal reductions must take priority. Businesses should upgrade to energy-efficient infrastructure, shift to renewable power, and optimize logistics. For example, replacing diesel fleets with electric vehicles directly reduces Scope 1 emissions. Transitioning to clean energy lowers Scope 2 impacts. These reductions have a lasting and measurable effect.
Understanding the Limits of Carbon Credits
Offsets vary widely in quality. Some projects lack verification or permanence. For instance, planting trees without ensuring long-term protection is risky. If those forests are cut or burned, the stored carbon is released. Additionally, offset markets are loosely regulated. This inconsistency makes it difficult to prove climate impact. Businesses must therefore choose credits certified by trusted bodies like Verra or Gold Standard.
Offsets vs Science-Based Targets
Science-Based Targets (SBTs) offer a structured way to cut emissions. These targets align with climate models and Paris Agreement goals. Unlike offsets, SBTs require businesses to reduce emissions within operations and supply chains. Offsets can only cover a small percentage of residual emissions. Therefore, SBTs keep companies accountable and transparent.
Offset Programs Have a Role, But a Small One
Offsets should complement, not replace, internal action. They are useful for covering hard-to-abate emissions, such as those from certain industrial processes or global logistics. Companies can also support nature-based solutions to restore ecosystems. However, true climate leadership means reducing before offsetting. The right balance ensures credibility and real impact.
Choosing High-Quality Offsets
If offsets are used, they must be verified and permanent. Look for projects with third-party certification, long-term monitoring, and social co-benefits. For example, community-based reforestation or renewable energy installations with local employment benefits are ideal. Transparency matters, businesses should publicly disclose their offset strategy, project details, and annual impact.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid claiming carbon neutrality based solely on credits. Do not delay reduction efforts while waiting for better offset solutions. Also, resist the urge to buy the cheapest credits without verifying their quality. These shortcuts can lead to reputational risks, regulatory backlash, and stakeholder distrust.
Offsetting and Greenwashing Risks
Consumers and investors are increasingly aware of greenwashing. If sustainability claims are unsupported or misleading, they can damage brand credibility. Regulators may impose penalties, and customers may switch to more transparent brands. A genuine net zero strategy must include emissions data, third-party audits, and detailed reporting.
How to Build a Reliable Carbon Strategy
Start with accurate carbon accounting. Use tools like Persefoni, Watershed, or Normative to map Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. Then, develop a roadmap for reductions across operations, supply chains, and logistics. Set science-based targets. Only after aggressive internal reductions should offsets be used for remaining emissions. This layered approach ensures integrity.
ALSO READ
Conclusion: Think Reduction First, Offset Last
Carbon offset programs are not inherently bad. But they must not be your primary climate strategy. To truly reach net zero, companies must focus on reducing their emissions at the source. Offsets can support the journey, but only when used responsibly and transparently. Businesses that lead with reduction, backed by data and science, will stand out in the low-carbon economy.
Call to Action
✉️ Download our free Net Zero Playbook to access emission tracking templates, verified offset checklists, and science-based reduction guides.
