The Future of Sustainability Audits: Data Science & ESG
Forget the old, painfully slow, spreadsheet-driven approach to sustainability auditing. Today, everything has sped up. Because of intense regulatory mandates, demanding investors, and the undeniable urgency of climate risk, companies are scrambling for real-time, precise, and fully transparent ESG data in sustainability audit software.
When you factor in complex global expansions and winding supply chains, it’s clear that the old audit handbook just isn’t working anymore. This need for speed and accuracy has brought about a new reality: the powerful combination of data science and ESG auditing.
We’re now using sophisticated tools from automated carbon tracking to machine-learning-powered risk predictions to validate environmental progress, tighten compliance, and prove our claims. This data-driven approach to sustainability isn’t just a trend and is the absolute future of how we manage climate accountability.
Why Traditional Sustainability Audits Are Struggling
Classic auditing approaches revolve around annual reports and estimated averages. But the modern ESG landscape exposes several limitations:
1. Static Snapshot Data
Most audits reflect a moment in time, not continuous environmental impact.
2. Manual Data Entry Errors
Human input introduces bias, rounding errors, and inaccuracies.
3. Limited Scope 3 Visibility
Up to 90% of corporate emissions come from upstream and downstream partners, which are historically difficult to measure.
4. Slow Turnaround
Companies often wait months for actionable insights which are too late for agile improvements.
These gaps now carry financial and reputational risk. That’s why organizations are adopting sustainability audit software to automate and validate climate data with scientific precision.
The Rise of ESG Data Science
Data science strengthens ESG auditing by applying advanced analytics techniques to environmental datasets. It transforms raw information into auditable insights.
Core elements include:
- statistical modelling
- machine learning prediction
- anomaly detection
- pattern recognition
- lifecycle analysis
Together, these capabilities provide auditors with high-resolution environmental intelligence.
Data Science: The Engine of Modern Auditing

Data science technologies, including Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, are the foundational components of next-generation sustainability audit software. They offer capabilities that are fundamentally impossible to replicate manually, elevating the audit from a historical review to a predictive, real-time process.
1. Automated Data Collection and Normalization
A major hurdle in ESG reporting is the lack of standardized, easily collectible data across a global enterprise and its value chain. Data science-driven ESG sustainability software addresses this by:
Automating Extraction: Using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to read and extract relevant metrics from unstructured documents like energy bills, supplier contracts, and policy documents.
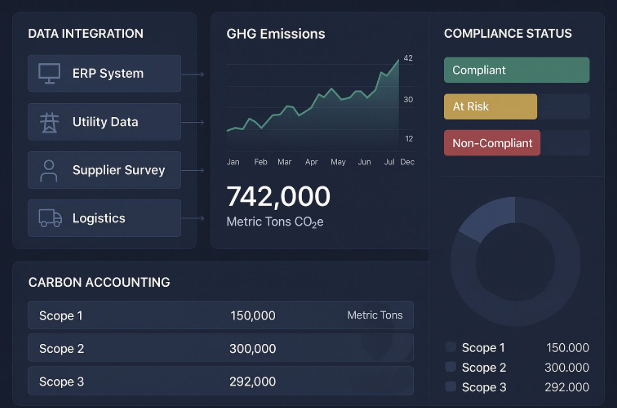
Integration: Connecting directly to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, operational databases, and utility providers to collect data in real-time, bypassing manual input and spreadsheets.
Normalization: Applying consistent, up-to-date emissions factors and reporting frameworks (e.g., GHG Protocol, GRI, SASB) to all raw data, ensuring apples-to-apples comparison across different facilities and time periods.
2. Scientific Carbon Accounting and Emissions Audit Tools
The precision required for carbon tracking audits is being met by advanced models. Machine Learning (ML) is particularly effective in addressing the most challenging emissions category: Scope 3 (value chain emissions).
Predictive Modeling: ML algorithms can use a company’s financial data, industry benchmarks, and historical Scope 1 and 2 data to create highly accurate estimations for missing or difficult-to-measure Scope 3 emissions (such as purchased goods and services, and employee travel).
Anomaly Detection: AI-powered systems continuously monitor real-time data from IoT devices and sensors to flag unexpected spikes in energy use or emissions. This real-time auditing capability allows companies to detect operational inefficiencies and potential compliance breaches instantly, shifting from reactive to preventive sustainability management.
Scenario Analysis: Advanced analytics can simulate the impact of various climate transition risks (e.g., a carbon tax, extreme weather events, or a shift to new energy sources) on a company’s emissions trajectory and financial performance, enabling truly scientific ESG audits that look forward, not just backward.
Also See: Environmental Science Meets Carbon Accounting Software: A Perfect Match
3. Improved Audit-Readiness and Assurance
The core function of the audit is trust. Data-driven sustainability platforms are embedding audit trails and assurance workflows directly into the data management process.
Data Lineage: The software maintains a complete, immutable record of every data point, showing its source, the transformation or calculation applied, and the individual responsible for its validation. This transparent audit trail makes the external verification process significantly faster and more reliable.
Governance Workflows: Dedicated features enforce internal controls, such as mandatory approval by data owners before a metric is finalized and reported, ensuring the integrity of the information presented to external auditors.
Scientific ESG Audits: What Makes Them Different?
A scientific ESG audit relies on measurable, verifiable environmental data instead of estimates.
Differentiators include:
- Empirical Data Validation
- Measurements from sensors, not surveys.
- Lifecycle Assessment Models
- Cradle-to-grave impact analysis.
- Standardized Carbon Factors
- Consistent calculations across industries.
- Predictive Analytics
- Forecast future emissions based on current activity.
Scientific ESG audits empower companies to:
- verify ESG claims
- avoid penalties
- attract sustainable investment
They show real environmental stewardship, not marketing spin.
The New Role of the Auditor: From Verifier to Strategist

The integration of data science and ESG sustainability software fundamentally changes the role of the human auditor. They will no longer spend the majority of their time sample-checking spreadsheets. Instead, they will focus on:
A. Validating Models and Methodology
The future auditor will need a deep understanding of the underlying data science models. Their expertise will be in validating the integrity of the algorithms, the selection of emissions factors, and the robustness of the data lineage ensuring the calculations are scientifically sound and aligned with regulatory requirements.
B. Contextual Interpretation and Risk Assessment
With automated tools handling data ingestion and calculation, auditors can dedicate their time to high-value activities: interpreting the meaning of the data, assessing material risks, and evaluating the effectiveness of a company’s governance structure in managing those risks. This includes assessing the social (S) and governance (G) factors, where qualitative data analysis and expert judgment remain critical.
C. Driving Strategic Insight
The real-time, predictive nature of data-driven sustainability allows the auditor to become a key strategic advisor. By identifying trends and vulnerabilities within the data such as a specific supply chain tier responsible for the majority of Scope 3 emissions which can offer actionable recommendations for decarbonization and efficiency improvements, turning the audit from a compliance exercise into a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
The way we handle corporate responsibility is going through a massive change. Merging data science with ESG isn’t just a gradual shift; it’s a total overhaul in how we hold companies accountable. We’re finally moving past slow, manual processes and embracing automated, scientific, and continuous assurance.
By adopting this kind of carbon audit technology and scientific audit software, companies can stop focusing only on basic compliance. Instead, they can build genuine, data-driven sustainability which is the best way to earn investor confidence, create business resilience, and lay a truly credible foundation for a sustainable future.
FAQ: Sustainability Audit Software
What is a scientific ESG audit?
A scientific ESG audit uses empirical data and analytics to verify environmental performance.
How does data science improve carbon tracking?
It enhances precision using statistical models, sensors, and real-time data ingestion.
Is scientific ESG software required for compliance?
Increasingly yes. Regulatory frameworks are pushing toward proof-based reporting.